Research
Electroencephalogram (EEG): an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain’s surface; measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
CT scan (CAT scan): series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body
PET scan (positron emission tomography): visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task; shows us what parts of the brain work when we perform different mental tasks
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see the structure of the brain
fMRI (functional MRI): tracks blood flow from multiple MRIs taken in succession in order to indicate brain activity; allows us to see structures and function
Lower Brain
Brain stem: oldest part and central core of the brain; begins where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; responsible for automatic survival functions; cross over point where most nerves to and from each side of the brain connect with the body’s opposite side
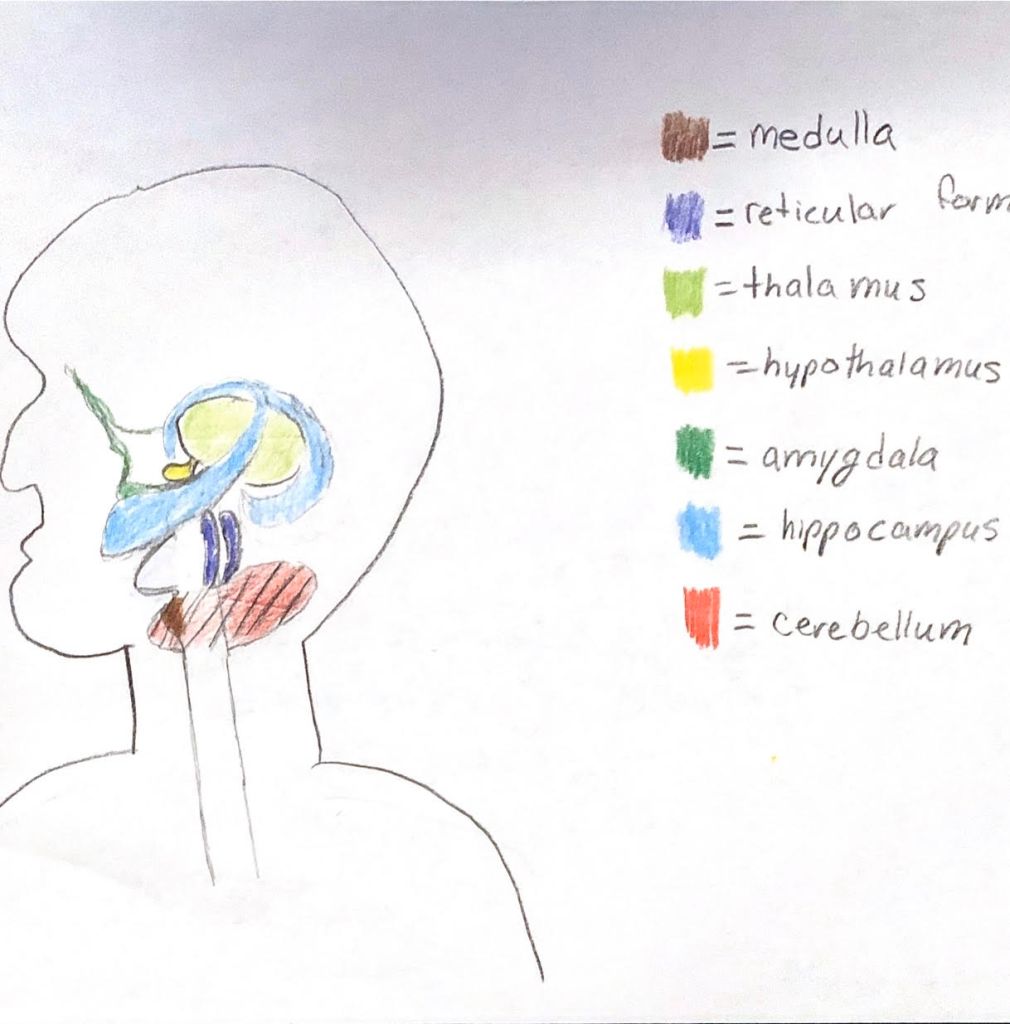
Medulla: base of the brain stem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Reticular Activating system: nerve network in the brain stem that plays an important role in controlling arousal; filters incoming stimuli and relays important information to other areas of the brain
Thalamus: sensory switchboard; located on the top of the brain stem; directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex
Cerebellum: “little brain;” helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance; involved in learning behaviors and memory of that learning
Mid-brain
Limbic system: doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brain stem and cerebral hemispheres
- Amygdala: almond-shaped structures linked to emotions such as aggression and fear
- Hypothalamus: neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs basic needs for survival (eating, drinking, body temperatures); linked to emotion (fear, aggression) and triggers autonomic nervous system activity
- Hippocampus: linked to memory
Cerebral Cortex: intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres
Frontal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; functions – speaking, muscle movement, higher-order thinking (planning, judgement), personality; motor cortex – controls voluntary movements
Parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; functions – process sensory information; somatosensory cortex – processes body touch and movement sensations
Occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; function – vision
Temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; functions – audition (hearing) and language comprehension