Nervous system: electro-chemical communication of the body; made up of nerve cells (neurons) divided into 2 systems
Central Nervous System (CNS): the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System: neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Reflex: a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus
Types of Neurons
Sensory neurons: carry incoming info from the sense receptors to the CNS (body to brain)
Inter-neurons: CNS neurons that internally communicate within the brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons: carry outgoing info from the CNS to muscles and glands (brain to body)
Neuron: a nerve cell; building block of the nervous system
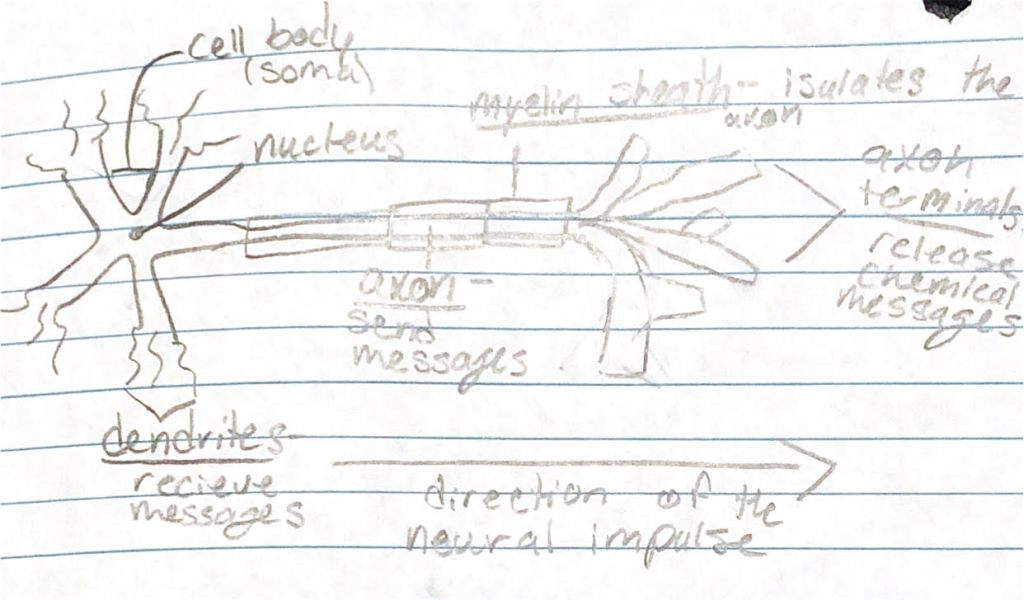
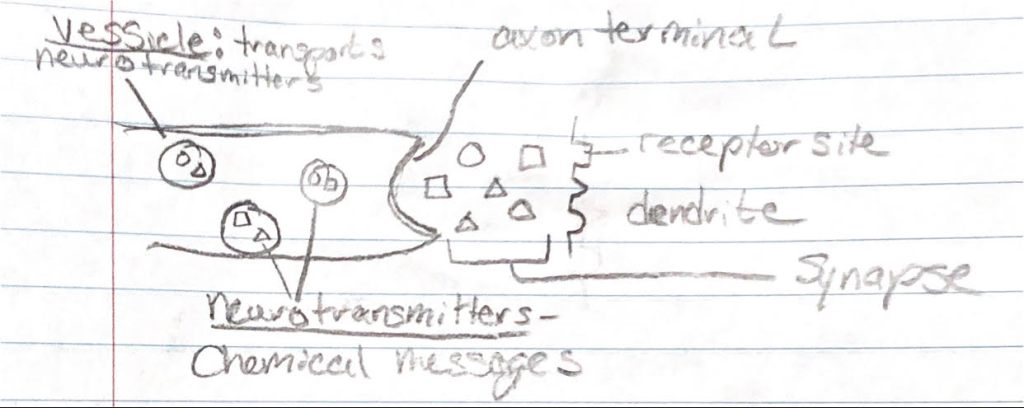
Action potential: a brief electrical charge that moves down an axon (all or none response)
Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Synapse: space between the axon of one neuron and dendrites of another; often called the synaptic gap (less than one millionth of an inch!)
Re-uptake: neurotransmitters return to sending neurons
Neural networks: clusters of neurons that work together; each neuron connects with roughly 10,000 others
Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine: triggers muscle contractions; involved in learning and memory (linked with Alzheimer’s)
Endorphins: natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters; linked to pain control and pleasure
Dopamine: influences movement, attention and emotion; linked to Parkinson’s Disease (not enough dopamine) and schizophrenia (overly active dopamine neurotransmitters)
Serotonin: affects mood, hunger, sleep and alertness
Agonist: mimics neurotransmitters and fills endorphin receptor sites and sends the message (like opiods)